Whether you reside within the quickly drying American West or are aboard the International Space Station for a six-month stint, having sufficient water to stay on is a continuing concern. As local weather change continues to play havoc on the West’s aquifers, and as humanity pushes additional into the photo voltaic system, the potable provide challenges we face in the present day will solely develop. , a few of NASA’s cutting-edge in-orbit water recycling analysis is coming again right down to Earth.
On Earth
In California, for instance, the from the state’s properties and companies, storm drain and roof-connected runoff, makes its method by greater than 100,000 miles of sewer strains the place it — barring — finally finally ends up at one of many state’s 900 wastewater therapy crops. How that water is processed relies on whether or not it’s destined for human consumption or non-potable makes use of like agricultural irrigation, wetland enhancement and groundwater replenishment.
takes a multi-step strategy to reclaiming its potable wastewater. Large solids are first strained from incoming fluids utilizing mechanical screens on the therapy plant’s headworks. From there, the wastewater flows right into a settling tank the place a lot of the remaining solids are eliminated — sludged off to anaerobic digesters after sinking to the underside of the pool. The water is then despatched to secondary processing the place it’s aerated with nitrogen-fixing micro organism earlier than being pushed into one other settling, or clarifying, tank. Finally it’s filtered by a tertiary cleansing stage of cationic polymer filters the place any remaining solids are eliminated. By 2035, whereas Aurora, Colorado, and Atlanta, Georgia, have each already begun augmenting their consuming water provides with potable reuse.
“There are additional benefits beyond a secure water supply. If you’re not relying on importing water, that means there’s more water for ecosystems in northern California or Colorado,” Stanford professor William Mitch, stated in . “You’re cleaning up the wastewater, and therefore you’re not discharging wastewater and potential contaminants to California’s beaches.”
Wastewater therapy crops in California face various challenges, the notes, together with growing old infrastructure; contamination from improperly disposed prescribed drugs and pesticide runoff; inhabitants calls for mixed with diminished flows resulting from local weather change-induced drought. However their capability to ship pristine water really outperforms nature.
“We expected that potable reuse waters would be cleaner, in some cases, than conventional drinking water due to the fact that much more extensive treatment is conducted for them,” Mitch argued in an October research in . “But we were surprised that in some cases the quality of the reuse water, particularly the reverse-osmosis-treated waters, was comparable to groundwater, which is traditionally considered the highest quality water.”
The solids pulled from wastewater are additionally closely handled throughout recycling. The junk from the primary stage is shipped to native landfills, whereas the organic solids strained from the second and third phases are despatched to anaerobic chambers the place their decomposition generates that may be burned for electrical manufacturing and transformed to nitrogen-rich fertilizer for agricultural use.
New York, for instance, from its 1,200-plus statewide wastewater therapy crops (WWTPs). However, lower than a tenth of crops (116 particularly) really use that sludge to provide biogas, per a 2021 report from the , and is “mainly utilized to fuel the facilities and for the combined heat and power generation of the WWTPs.”
Non-potable water might be handled much more immediately and, in some instances, . Wastewater, rainwater and can like water the foyer crops and flushing bogs after being captured and handled in an (ONWS).
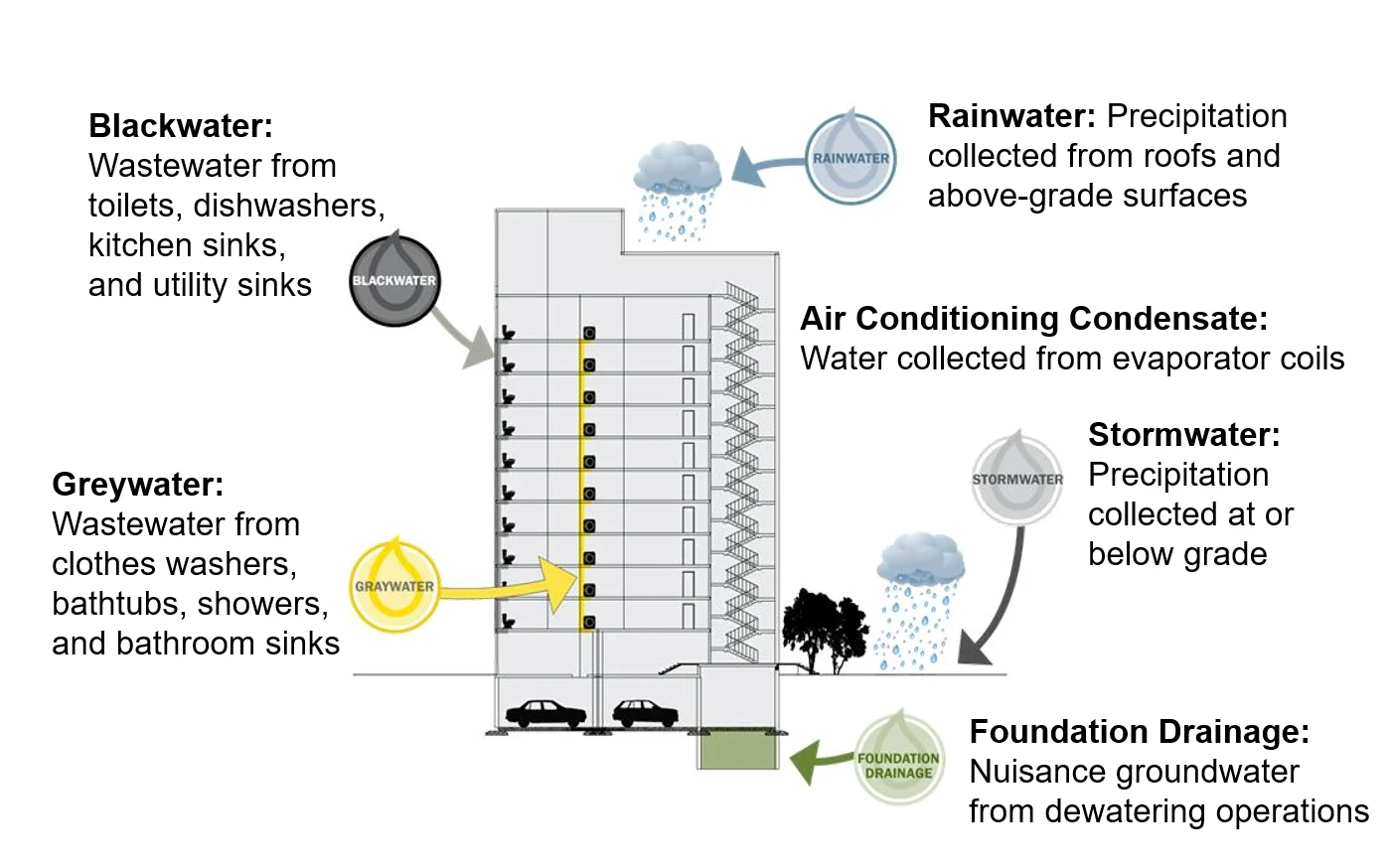
EPA
“Increasing pressures on water resources have led to greater water scarcity and a growing demand for alternative water sources,” the . “Onsite non-potable water reuse is one solution that can help communities reclaim, recycle, and then reuse water for non-drinking water purposes.”
In Orbit
Aboard the ISS, astronauts have even much less leeway of their water use on account of the station being a closed-loop system remoted in area. Also as a result of SpaceX expenses $2,500 per pound of cargo (after the primary 440 kilos, for which it expenses $1.1 million) to ship into orbit on one in all its rockets — and liquid water is heavy.

ESA
While the ISS does get the occasional cargo of water within the type of 90-pound duffle bag-shaped Contingency Water Containers to switch what’s invariably misplaced to area, its inhabitants depend on the difficult internet of levers and tubes you see above and beneath to reclaim each dram of moisture attainable and course of it into potability. The station’s Water Processing Assembly can produce as much as 36 gallons of drinkable water every single day from the crew’s sweat, breath and urine. When it was put in in 2008, the station’s water supply wants . It works along side the Urine Processor Assembly (UPA), Oxygen Generation Assembly (OGA), Sabatier reactor (which recombines free oxygen and hydrogen break up by the OGA again into water) and Regenerative Environmental Control and Life Support Systems (ECLSS) techniques to take care of the station’s “” and . Cosmonauts within the Russian phase of the ISS depend on a separate filtration system that solely collects bathe runoff and condensation and due to this fact require extra common water deliveries to maintain their tanks topped off.
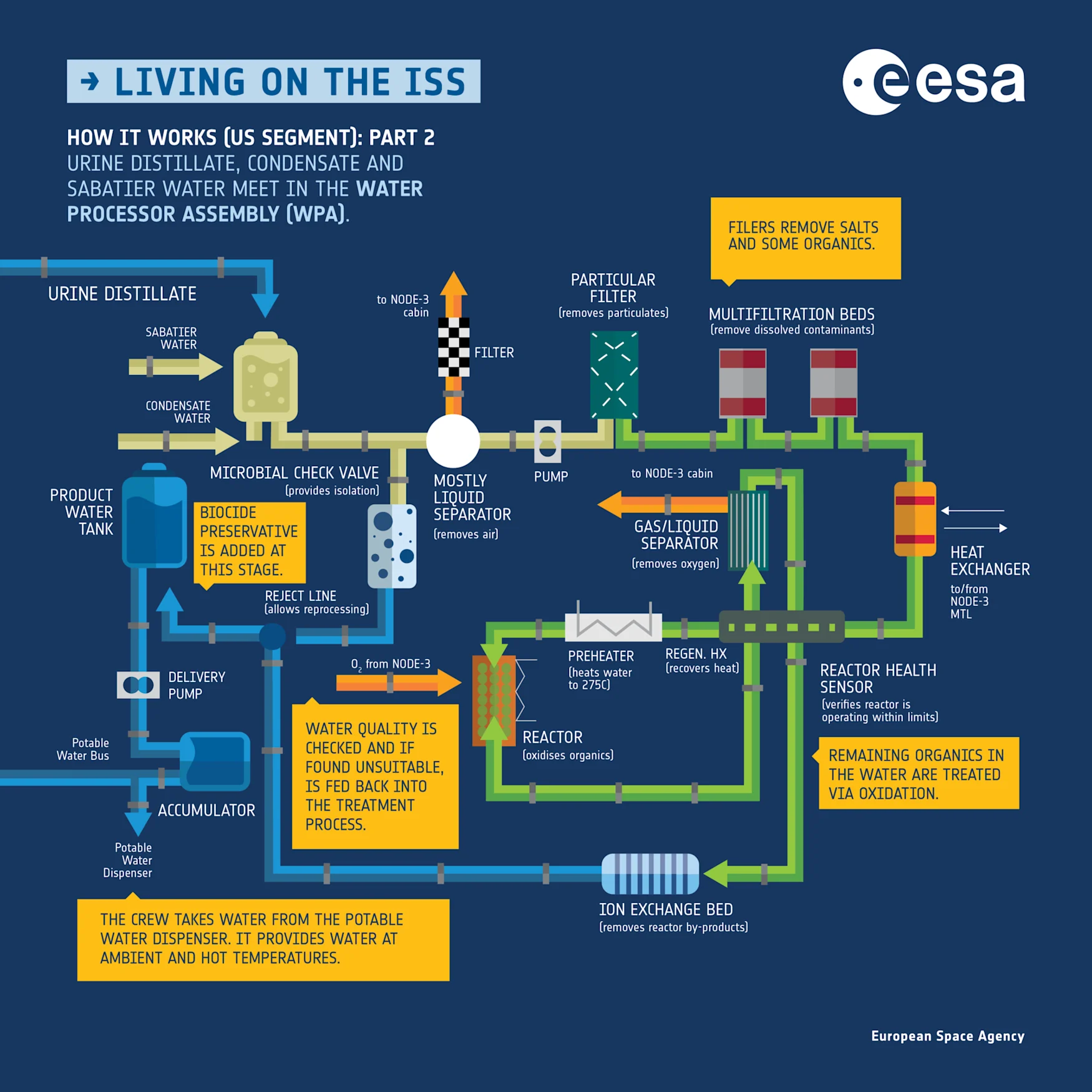
ESA
In 2017, NASA upgraded the WPA with a brand new reverse-osmosis filter to be able to, “reduce the resupply mass of the WPA Multi-filtration Bed and improved catalyst for the WPA Catalytic Reactor to reduce the operational temperature and pressure,” the company introduced that 12 months. “Though the WRS [water recovery system] has performed well since operations began in November 2008, several modifications have been identified to improve the overall system performance. These modifications aim to reduce resupply and improve overall system reliability, which is beneficial for the ongoing ISS mission as well as for future NASA manned missions.”
One such enchancment is the upgraded Brine Processor Assembly (BPA) delivered in 2021, a filter that sieves extra salt out of astronaut urine to provide extra reclaimed water than its predecessor. But there may be nonetheless an extended approach to go earlier than we will securely transport crews by interplanetary area. NASA notes that the WPA that obtained delivered in 2008 was initially rated to get well 85 p.c of the water in crew urine although its efficiency has since improved to 87 p.c.
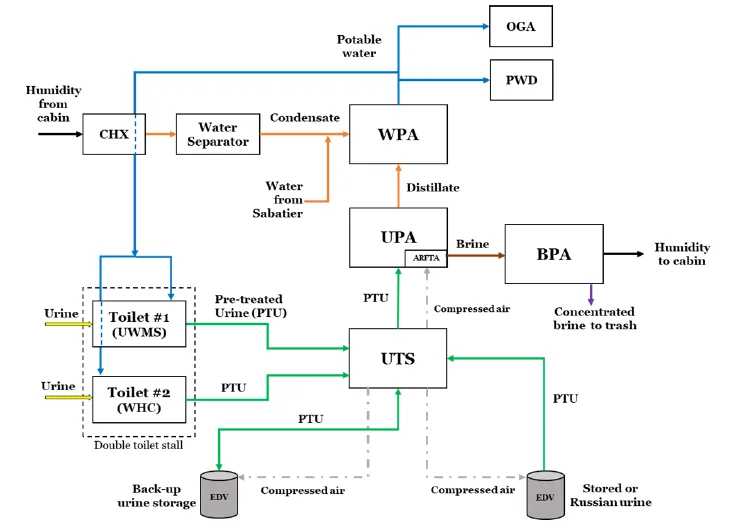
NASA
“To leave low-Earth orbit and enable long-duration exploration far from Earth, we need to close the water loop,” Caitlin Meyer, deputy mission supervisor for Advanced Exploration Systems Life Support Systems at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, added. “Current urine water recovery systems utilize distillation, which produces a brine. The [BPA] will accept that water-containing effluent and extract the remaining water.”
When the post-processed urine is then blended with reclaimed condensation and runs by the WPA once more, “our overall water recovery is about 93.5 percent,” Layne Carter, International Space Station Water Subsystem Manager at Marshall, . To safely get to Mars, NASA figures it wants a reclamation charge of 98 p.c or higher.
But even when the ISS’s present state-of-the-art recycling expertise isn’t fairly sufficient to get us to Mars, it’s already making an impression planetside. For instance, within the early 2000’s the Argonide firm developed a “NanoCeram” nanofiber water filtration system with NASA small enterprise funding assist. The filter makes use of positively charged microscopic alumina fibers to take away nearly all contaminants with out overly limiting circulation charge, finally spawning .
“The shower starts with less than a gallon of water and circulates it at a rate of three to four gallons per minute, more flow than most conventional showers provide,” . “The system checks water quality 20 times per second, and the most highly polluted water, such as shampoo rinse, is jettisoned and replaced. The rest goes through the NanoCeram filter and then is bombarded with ultraviolet light before being recirculated.” According to the Swedish Institute for Communicable Disease Control, the ensuing water is cleaner than faucet.
All merchandise advisable by Engadget are chosen by our editorial workforce, unbiased of our father or mother firm. Some of our tales embrace affiliate hyperlinks. If you purchase one thing by one in all these hyperlinks, we could earn an affiliate fee. All costs are right on the time of publishing.
#Water #recycling #applied sciences #developed #area #serving to #parched #American #west #Engadget